Advancements are coming to industrial Ethernet, including emerging technologies like Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) and more established Ethernet with Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN).

Industrial Ethernet insights
- Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) simplifies connectivity for compact devices by reducing wiring.
- Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) enhances Ethernet’s real-time capabilities with precise timing and low latency, benefiting applications like robotics and automation.
- Adoption of TSN over Ethernet is already underway.
Emerging industrial automation technologies like Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) and Ethernet with Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) are set to redefine industrial communication and connectivity. Single Pair Ethernet allows devices to transmit data and power over a single twisted pair of wires, significantly simplifying connectivity for compact devices and sensors in smart factories and industrial settings.
This technology reduces wiring complexity, enabling more efficient and scalable networks across a wide array of devices. Ethernet with TSN, on the other hand, enhances Ethernet’s capability to handle real-time data by adding timing synchronization and prioritizing data packets. This enables precise, low-latency communication critical for applications like robotics, automation and autonomous systems. Together, SPE and Ethernet with TSN facilitate seamless, fast and reliable data exchange in Industry 4.0 environments, allowing for unprecedented levels of automation, flexibility and efficiency in industrial operations.
Although SPE holds significant potential to streamline network infrastructure, especially for compact devices and sensors in industrial environments, it’s still a newer specification. Industry experts suggest that it may take some time before SPE-based products and solutions are widely available across sectors.
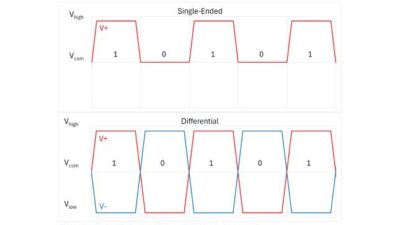
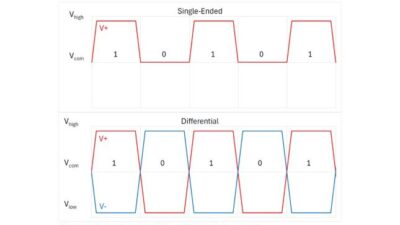
Unlike SPE, the specification for TSN over Ethernet is fully developed and adoption has already been underway. TSN provides enhanced Ethernet capabilities with precise timing and synchronization, allowing deterministic data transfer that is essential for real-time industrial applications like robotics, autonomous systems and factory automation (see Figure 1).

How TSN impacts real-time data transmission
With TSN, various industries have started implementing reliable, low-latency communication solutions, benefiting from the now standardized protocols that ensure interoperability across devices and systems. The maturity of the TSN standards enables manufacturers to deploy it in settings where precise timing and minimal latency are critical, giving it a considerable head start over SPE in terms of real-world application. This rapid adoption of TSN Ethernet demonstrates its readiness and immediate impact on industrial automation.
Ethernet with Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) brings specific technical attributes to Ethernet that enable real-time data transmission with high reliability and precision. Key attributes and benefits include:
Deterministic data transmission: TSN ensures that data packets are delivered predictably within strict timing windows, which is crucial for applications requiring synchronized operations, such as robotics and automated machinery in industrial environments. Determinism is achieved through time synchronization and traffic scheduling protocols, allowing TSN-enabled devices to manage data flows precisely, even under high network load .
Time synchronization: TSN uses protocols like IEEE 802.1AS to provide high-precision clock synchronization across networked devices, maintaining microsecond-level timing accuracy. This feature is essential for coordinated, latency-sensitive processes in automation, such as motion control and vision systems, where timing discrepancies can disrupt operations .
Traffic prioritization and Quality of Service (QoS): Through mechanisms like IEEE 802.1Qbv, TSN assigns priority levels to different data types, ensuring high-priority, time-sensitive data reaches its destination without interruption. This QoS approach allows for a mix of data types—such as control, video and general information — over a single network, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing the need for separate infrastructures
Interoperability: As TSN is built on Ethernet, it seamlessly integrates with existing Ethernet-based networks, allowing for flexible and scalable solutions. This interoperability supports Industry 4.0 goals by connecting diverse devices and systems across manufacturing and industrial environments without requiring specialized cabling or network structures.
These features make TSN Ethernet a versatile, high-performance solution for industries needing precise, real-time control, typically in motion-related applications.
TSN is invaluable for automating complex manufacturing processes that involve real-time, coordinated operations. It ensures low-latency and synchronized communication between sensors, controllers and actuators, essential in assembly lines and robotic systems where split-second timing impacts quality and efficiency .
Industry-specific TSN applications
In robotics, TSN’s precise timing and low latency ensure seamless operation between robotic arms, sensors and controllers. TSN supports coordinated multi-axis motion control and complex robotic movements, which are critical in high-speed packaging, welding and pick-and-place applications.
TSN is used in automotive applications for safety-critical communication between electronic control units (ECUs), particularly in autonomous vehicles. It enables reliable data exchange among sensors, cameras and AI processors, which are essential for real-time decision-making and safe navigation in autonomous and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
How network standards will influence the path to TSN adoption
Vendors adopt Ethernet with Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) by implementing TSN-compliant hardware and software into their industrial communication solutions. Adoption often includes upgrading network components — such as switches, controllers and network interface cards — with TSN capabilities like time synchronization and traffic prioritization. This requires manufacturers to align with IEEE standards (e.g., IEEE 802.1AS for time synchronization and IEEE 802.1Qbv for traffic scheduling), ensuring interoperability across TSN devices from different vendors. Adopting TSN allows vendors to deliver solutions that meet the high reliability and low-latency requirements of industries that demand real-time data exchange, such as automotive manufacturing and process automation.
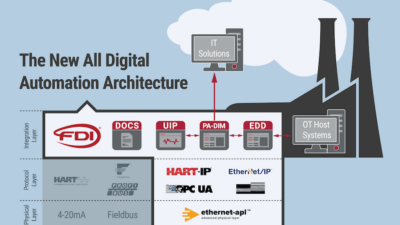
The CC-Link Partner Association (CLPA) plays a crucial role in facilitating TSN adoption by setting interoperability standards and providing a collaborative platform for vendors to test and certify their TSN-enabled products. CLPA’s CC-Link IE TSN protocol is one of the first open industrial networks to integrate TSN technology. It extends Ethernet with TSN’s real-time communication capabilities, supporting seamless data exchange and coordination across production lines. By offering certification for TSN-compatible products, CLPA helps ensure that devices from different vendors can work together reliably, accelerating TSN adoption across industries (see Figure 2) .

The TSN Industrial Automation Conformance Collaboration (TIACC) is a joint initiative by major industrial organizations like the CC-Link Partner Association (CLPA), Avnu Alliance, ODVA, OPC Foundation and Profibus & Profinet International. Its purpose is to create a unified conformance test plan for devices using Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN), specifically aligning with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)/IEEE 60802 profile. This effort aims to enable interoperability between TSN-compatible products from different vendors, ensuring they can operate seamlessly on the same network infrastructure in industrial environments.
The TIACC collaboration directly impacts the adoption of TSN by standardizing testing processes and providing assurance that TSN-based devices will work together reliably, regardless of manufacturer. This collaboration is crucial for industries aiming for network convergence, where various industrial and IT protocols can coexist on a single network, enhancing efficiency and simplifying network management. By validating interoperability, TIACC enables industries like automotive, pharmaceutical and food and beverage to confidently integrate TSN for applications that require high precision and real-time performance, supporting Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing goals .
SPE and TSN are transforming industrial automation
In summary, emerging technologies like Single Pair Ethernet (SPE) and Ethernet with Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) are transforming industrial automation by improving connectivity and real-time communication capabilities. While SPE promises simplified wiring and scalable networks, particularly for compact devices in industrial settings, its adoption is expected to take time as the technology matures. Conversely, TSN’s specifications are fully established, enabling deterministic, low-latency communication essential for automation and robotics applications.
Already seeing wide adoption, TSN allows for interoperable, high-precision networks supporting synchronized data transmission across various devices and industries. Initiatives like the TSN Industrial Automation Conformance Collaboration (TIACC), led by organizations including the CC-Link Partner Association (CLPA), are driving industry-wide standards for interoperability, helping to accelerate TSN adoption. This collaborative approach supports the integration of industry 4.0 technologies across sectors, fostering efficient, reliable and scalable industrial operations for the future.
Thomas J. Burke is the global strategic advisor for CC Link Partner Association (CLPA). Edited by Sheri Kasprzak, managing editor, Automation & Controls, WTWH Media.